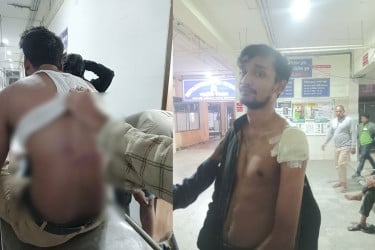
Grammar
Use of Need
Need as an auxiliary verb and an ordinary verb. Need is used both as a principal verb and as an auxiliary: When need is used as a principal verb, it means ‘require’.
Ex.-He needs my help.
We need two more players for the team.
We have got what we need.
He needed some more time to decide the question.
When need is used as an auxiliary verb, its form remains the same whatever be the number or person of the subject. The auxiliary need is common in questions and negatives.
Ex. He need not ask my permission.
He need not wait any longer.
They need not make such a fuss over it.
You need not mention this to anyone else.
Sometimes it is used with hardly:
Ex.-I need hardly say that I am very grateful.
We need hardly remind you of your promise to visit us.
I need hardly add that you are always welcome.
It can be used with only:
Ex.-He need only say what he wants and it will be granted.
You need only sign this form and I shall do the rest.
I need only add that we shall always remain indebted to you for your help.
Need is usually used in questions without ‘not’.
Ex.-Need he wait any longer?
Need I come again?
He need not wait any longer, need he?
If the answer is in the negative, we will say:
‘No, he / you / they need not.’
But if the answer is in the positive, you should say:
‘Yes, he /she / you must.’
The opposite of need not in such a context is not need but must.
Need without not is also used in the following kinds of statements:
Ex.-You need pay only 20 dollars.
I don’t think we need copy all these figures.
There need be no further correspondence.
Subject-verb Agreement
Example:
The list of items is/are on the desk.
Being able to identify the subject and verb correctly will also help you with commas and semicolons as you will see later.
Definition:
A verb is a word that shows action (runs, hits, and slides) or state of being (is, are, was, were, am, and so on).
Examples:
He ran around the block.
You are my friend.
Rule 1
If a verb follows to, it is called an infinitive phrase and is not the main verb. You will find the main verb either before or after the infinitive phrase.
Examples:
I like to walk.
The efforts to get her elected succeeded.
Definition:
A subject is the noun or pronoun that performs the verb.
Example:
The woman hurried.
Woman is the subject.
Rule 2
A subject will come before a phrase beginning with of.
Example:
A bouquet of yellow roses will lend color and fragrance to the room.
Rule 3
To find the subject and verb, always find the verb first. Then ask who or what performed the verb.
Examples:
The jet engine passed inspection.
Passed is the verb. Who or what passed? The engine, so engine is the subject. If you included the word jet as the subject, lightning will not strike you. Technically, jet is an adjective here and is part of what is known as the complete subject.
From the ceiling hung the chandelier.
The verb is hung. Now, if you think ceiling is the subject, slow down. Ask who or what hung. The answer is chandelier, not ceiling. Therefore, chandelier is the subject.
Rule 4
Any request or command such as “Stop!” or “Walk quickly.” has the understood subject you because if we ask who is to stop or walk quickly, the answer must be you.
Example:
(You) Please bring me some coffee.
Bring is the verb. Who is to do the bringing? You understood.
Rule 5
Sentences often have more than one subject, more than one verb, or pairs of subjects and verbs.
Examples:
I like cake and he likes ice cream.
Two pairs of subjects and verbs
He and I like cake.
Two subjects and one verb.
She lifts weights and jogs daily.
One subject and two verbs.